“It’s ridiculous that time and time again we need a radioactive cloud coming out of a nuclear power-station to remind us that atomic energy is extraordinarily dangerous.”
Pierre Schaeffer, Composer
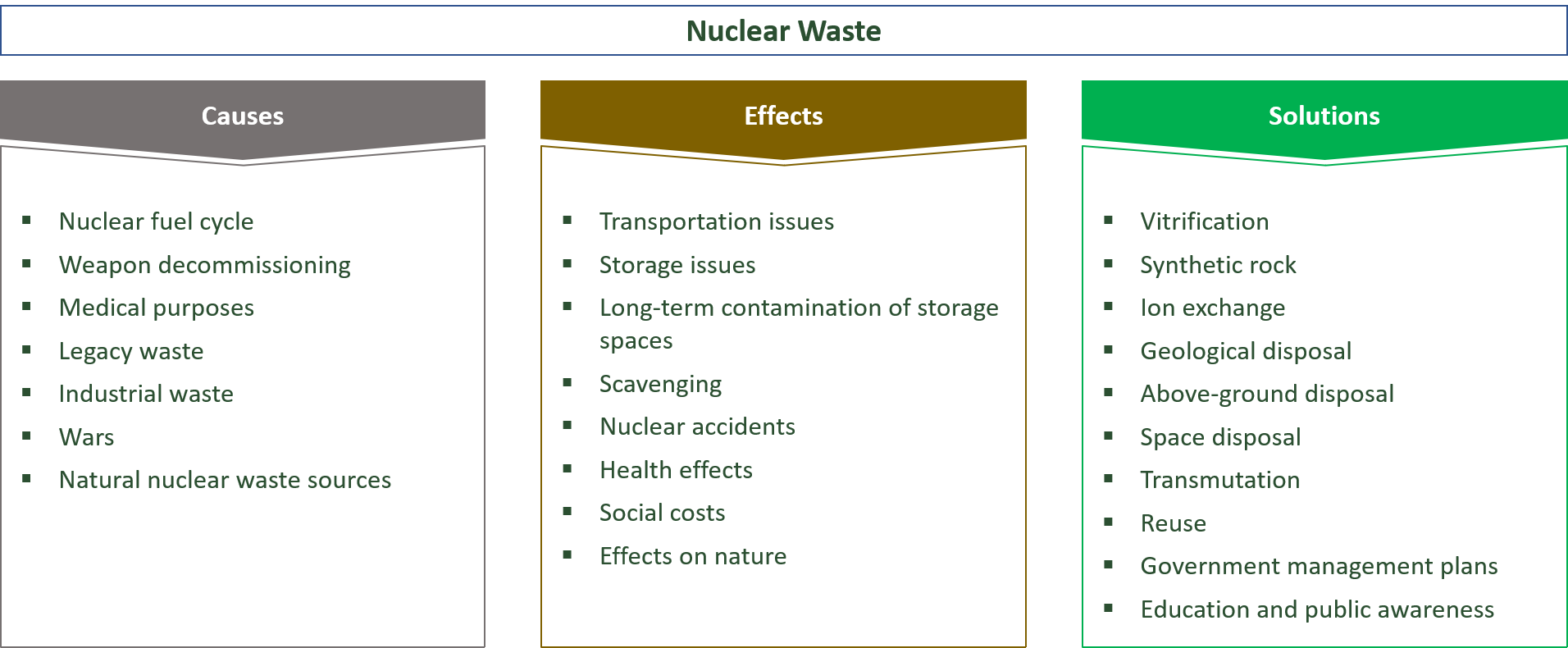
Nuclear Waste: Causes, Effects & Solutions
Nuclear waste can be defined as garbage that contains radioactive material.
Radioactive waste can display a serious threat to humanity and the whole environment since it takes quite a long time to decay.
Therefore, nuclear waste is subject to strict government regulations in order to prevent any adverse issues.
Audio Lesson
Contents
Types of Radioactive Waste
Mill tailings
Mill tailings are usually waste by-products of the processing of uranium-bearing ore.
They often consist of thorium, uranium and radium.
Although they are not highly radioactive, mill tailings have long half-lives and therefore it takes quite a long time for them to entirely decay.
Low-level nuclear waste
Low-level nuclear waste includes clothing, filters, paper and other materials which exhibit small amounts of radioactivity.
Low-level radioactive waste is usually a by-product of hospitals or industrial processes.
Materials which got in touch with low-level nuclear risk areas are precautionarily designated as low-level waste (LLW), however, they do not pose a risk to human health in most cases.
Although some of the LLWs require shielding for handling and transportation purposes, most of the LLWs are suitable for shallow land burial.
Intermediate-level nuclear waste
Since intermediate-level nuclear waste exhibits higher levels of radioactivity, it requires shielding.
However, there is no need for cooling in most cases.
Intermediate-level waste includes, among others, materials from reactor decommissioning as well as chemical sludge.
Long-lived intermediate-level waste is usually disposed of in geological repositories, while short-lived intermediate waste may be buried in shallow repositories.
Transuranic waste
Transuranic waste is defined as nuclear waste contaminated with alpha-emitting transuranic radionuclides with concentrations greater than 100 nCi/g and half-lives greater than 20 years, but which are also not classified as high-level nuclear waste.
Due to its longer half-live, transuranic waste is disposed of with more caution than low- or intermediate-level waste.
Transuranic waste usually is the by-product of the manufacturing process of nuclear weapons.
Transuranic nuclear waste is currently mainly disposed of in deep salt formations.
High-level nuclear waste
High-level radioactive waste is usually by-product in the generation of electricity in nuclear power plants.
The disposal process for high-level nuclear waste is subject to discussion by leading scientists.
Many of them advocate a solution in which the high-level nuclear waste is buried in either deep boreholes or in mines.
Nuclear Waste Disposal
Depending on the category and the classification of nuclear waste, it can be disposed of in several different ways.
As mentioned above, most disposal tactics include the burial or storage in mines.
Since the classification also varies by country, different countries may also treat the disposal process differently.
This can lead to great problems since if radioactive waste is not disposed of appropriately, due to their long half-lives, the contaminated areas could be lost for other purposes for a quite long time.

Causes for Nuclear Waste
- Nuclear fuel cycle
- Arms decommissioning
- Medical purposes
- Legacy waste
- Industrial waste
- Conflicts
- Natural nuclear waste sources
Nuclear fuel cycle
Radioactive waste is produced during the nuclear fuel chain.
The nuclear fuel chain describes the process of how radioactive fuel is extracted, processed, used and disposed of.
If the disposal process is not set up properly, large amounts of nuclear waste may be produced.
However, even if there is an effective nuclear waste disposal process, there are still some nuclear by-products which result in the production of nuclear waste.
Arms decommissioning
In the process of nuclear arms decommissioning, the radioactive substances which are left in arms have to be processed somehow.
As a result, many radioactive compounds will be left over after the decommissioning process.
These compounds have to be examined carefully and have to be classified appropriately before deciding how to deal with them.
Medical purposes
Radioactive waste is also produced in medical research and treatment facilities.
Examples include the treatment of thyroid cancer, lymphoma and bone cancer.
Radioactive compounds are also used for brachytherapy and external radiotherapy.
Legacy waste
Many areas that have been historically used for mining or military purposes are still contaminated with radioactive materials.
This waste has to be removed or stored somehow.
There are several cleanup programs that have the purpose of finding solutions on how to deal with the legacy waste.
Industrial waste
There are also some industrial processes that can cause radioactive waste.
Among others, this includes the process of radiography as well as applications such as oil well logging.
Conflicts
Although this will hopefully never happen again in the future, nuclear conflicts have a significant potential for the production of nuclear waste on a large scale.
This includes nuclear waste as a by-product of arm production.
Moreover, if nuclear arms are used, large areas of land will be contaminated for a quite long period of time.
Natural nuclear waste sources
There is also naturally occurring nuclear material in our environmental system.
These natural radioactive materials can lead to radioactive waste through the intervention of industrial processes.
For example, coal power plants emit small concentrations of radioactive compounds.
Moreover, the oil and gas industry also produces radioactive by-products like radium and radon.

Effects of Radioactive Waste
- Transportation issues
- Storage issues
- Long-term contamination of storage spaces
- Scavenging
- Nuclear accidents
- Health effects
- Social costs
- Effects on nature
Transportation issues
Although the transportation of radioactive waste is usually done with great care, there is a possibility for leaks or accidents related to the transport of radioactive material.
If this happens, radioactive material can contaminate the surrounding area and make it unusable for farming or other purposes in the near or also in the far future since many radioactive compounds have long half-lives which means that it takes quite long for them to entirely decay.
Storage issues
Radioactive waste is often stored in mills or other spaces deep in the ground.
If the storage processes are not executed with great care, there can be severe adverse effects on the surrounding environment.
If there are leaks in the storage space, radioactive material could contaminate the soil.
Moreover, through rainfalls, the radioactive compounds can also reach the groundwater and contaminate it which may lead to severe health issues not only for humans but also for many animals.
Thus, the inappropriate storage of radioactive waste can lead to huge adverse consequences for the whole ecological system.
Long-term contamination of storage spaces
Moreover, the storage spaces itself will be contaminated for a quite long period of time as well and we will not be able to use them for other purposes during this time.
Scavenging
The scavenging of abandoned nuclear materials leads to contamination of people dealing with these substances.
Since there is a market for many scavenged goods, especially in developing countries, people are willing to take the risk and make good amounts of money in the short term.
However, the long-term consequences are horrible since people get contaminated with radioactive compounds and will suffer diseases or in the worst case eventually die.
Moreover, many people are not even aware that the materials they are dealing with are indeed radioactive, thus having no idea how dangerous their behavior really is.
Making things worse, people who had been involved in scavenging may contaminate other people through daily interactions who had never been involved in scavenging activities.
Nuclear accidents
Nuclear accidents are a great threat to ecological systems as a whole.
Nuclear accidents can have severe adverse impacts and can lead to all sorts of pollution.
If there is an accident in a nuclear power plant, contaminated cooling water can reach the environment and contaminate the surrounding area.
Moreover, if there are explosions or other types of issues that cause radioactive material to get into the air, the consequences may be dramatic since the radioactive material can be carried through winds quite far and thus not only contaminate the near surroundings but also areas that are far away from the original accident location.
Health effects
The exposure to radioactive compounds can cause serious health problems or even death for humans as well as for all kinds of animals.
The main issue of radioactive compounds is that they are likely to cause cancer which in turn kills many people each year.
Moreover, scientists found that exposure to nuclear substances can change our DNA and thus alter the genes of future generations.
Social costs
There are great social costs related to radioactive waste.
Since radioactive waste usually has long half-lives, it contaminates storage spaces for a quite long time.
These areas can no longer be used for other purposes due to this contamination.
Moreover, if nuclear waste is not treated appropriately, it can harm the lives of people in a dramatic way.
Especially in poor countries, people are not aware of how dangerous nuclear waste really is and thus often get contaminated by scavenging activities.
Effects on nature
Radioactive waste has a significant adverse effect on nature.
Since radioactive waste is often stored in remote places which are the living space for many animals, these animals may become contaminated with radioactive material and thus suffer from the consequences.
Moreover, it may also alter the gene structure of animals and plants which may in turn hurt humans through the food chain.

Solutions to the Nuclear Waste Problem
- Vitrification
- Synthetic rock
- Ion exchange
- Geological disposal
- Above-ground disposal
- Space disposal
- Transmutation
- Reuse
- Government management plans
- Education and public awareness
Vitrification
For storing nuclear waste in a long-term manner, it has to be stabilized into a form in which it will not react nor degrade.
There is a process called vitrification which should accomplish this.
Vitrification is a process in which high-level waste is mixed with sugar and then calcined in order to stabilize the nuclear waste.
Synthetic rock
The synthetic rock method is another way to deal with nuclear waste which is currently developed for U.S. military waste.
The synthetic rock method includes the use of perovskite, hollandite and zirconolite.
These substances should bind the radioactive compounds and thus reduce their nuclear activity.
Ion exchange
Ion exchange is a method often used for medium-level active waste.
In this process, the radioactivity is concentrated into a small volume.
The remaining low-level nuclear waste can then be mixed with substances like cement to get a solid waste form.
Geological disposal
For a long-term solution, many scientists prefer the disposal of radioactive substances in stable geological formations between 500 and 1000 meters below the surface.
Mining techniques or tunnel boring machines should be used in order to dig tunnels in the ground.
The goal of geological disposal is to get rid of high-level radioactive waste by permanently isolate it from the human environment.
Above-ground disposal
Another form of disposal for radioactive waste is to seal it in a steel cylinder with inert gas and to place this construct in a concrete cylinder.
The concrete cylinder acts as a radiation shield and thus helps to mitigate the exposure of nuclear radiation to humans.
In contrast to geological disposal, the above-ground disposal method has some advantages.
It is relatively cheap and nuclear waste can be retrieved in later stages for reprocessing purposes.
Space disposal
Space disposal could be a method used to get rid of nuclear waste, but it seems not a practical method in the near future.
Space disposal means to bring the radioactive waste out of our atmosphere and just to drop it into space.
This would remove nuclear waste from our planet.
Although the idea seems to be quite promising, there are several problems related to it. In order to get the waste into space, many transportation vehicles have to be used.
This increases the probability that one of them will eventually fail.
A failure of a launch vehicle could potentially lead to catastrophic results, as it may lead to a spread of radioactive material over the whole planet, thus contaminate our whole environment.
The risk of this method seems to be too high in order to justify it.
Moreover, technology at this point in time is not sophisticated enough to accomplish this process in an economic manner.
It is just too expensive to carry out space disposal of nuclear waste compared to the alternatives.
Transmutation
Transmutation means transforming high-level nuclear waste into less-harmful, short-lived radioactive waste.
Although transmutation may be a valid instrument to get rid of radioactive compounds, it has its problems when applying it to practical situations.
Transmutation has been banned various times in history due to the possible dangers.
Right now, intensive research is done in order to develop the transmutation method further with the goal to eventually make it a valid method to deal with high-level active waste.
Reuse
Another way to deal with radioactive waste is to reuse it.
Reusing radioactive compounds doesn’t solve the problem of radioactivity, however, it may reduce the total amount of nuclear waste produced.
Government management plans
Governments worldwide are in charge to find solutions to the nuclear waste problem.
There are different approaches on how to deal with nuclear waste.
Moreover, there are big differences in the level of strictness in regulations.
Europe tends to be stricter than the U.S. when it comes to radiation limits than the U.S.
However, nuclear waste is a serious problem and potential issues with it could potentially spill over across borders.
Thus, governments should work together and present frameworks that are consistent with latest research and act according to that.
Education and public awareness
In order to mitigate the issue of radioactive waste, we also have to inform the public about the negative adverse consequences of nuclear waste.
We have to show them how this waste affects the living conditions of people and how it can potentially affect our whole environment.
By educating people about the adverse effects of nuclear waste, we could convince them to save energy in their daily lives and thus to contribute to a reduction in nuclear waste.
Therefore, it is crucial to start education already at young ages.
We have to show children in school how our energy is produced, what effect this energy production has on the environment and what everyone of us can do to mitigate this problem.
Children are then likely to also convince their parents to save energy.
Thus, the awareness concerning the issue of nuclear waste of the whole population will increase and therefore the behavior of many people will start to change their behavior in favor of a more resource-saving way of life.

Examples for Nuclear Accidents
1957 Windscale, UK
The Windscales Unit 1 caught fired and melted, which led to a release of large amounts of radioactive material in the surrounding environment.
It took three days to put out the fire.
It is estimated that this disaster had been responsible for around 200 deaths due to cancer.
1959 Sodium Reactor Experiment, USA
There had been a partial meltdown in Los Angeles due to a cooling blockage which led to overheating of the reactor.
1961 SL-1, USA
In Idaho in 1961, the removal of a control rod led to a power surge and steam explosion at a boiling water reactor and caused the death of all workers who had been present in this building.
1966 Enrico Fermi Unit 1, USA
A cooling blockage in the Enrico Fermi Unit 1 in Michigan in 1966 caused a partial meltdown of fuel assemblies.
The reactor was shut down for repairs after this incident and returned for operation in 1972, it was finally shut down in 1975.
1978 Three Mile Island, USA
In Pennsylvania, the Three Mile Island Unit 2 suffered a partial meltdown in 1978.
Although this meltdown only resulted in small amounts of radioactive material released into the environment, it is still considered as one of the most serious nuclear accidents in U.S. history.
1986 Chernobyl, Ukraine
In 1986, the worst nuclear accident in the history of mankind happened.
A sudden power surge led to an explosion and to a fire that destroyed Unit 4 of the reactor.
Massive amounts of radioactive material had been released in the air which caused serious health issues not only for people who lived nearby, but even for people far away in Europe since the wind had spread the nuclear particles thousands of miles.
Even today, there is some radiation left in Europe.
Scientists often warn people concerning the consumption of mushrooms in East Europe or even Central Europe since they may still be contaminated with radioactive material.
2011 Fukushima Daiichi, Japan
In 2011, Fukushima had been hit by an earthquake which resulted in a Tsunami.
This event caused serious damages to the Daiichi nuclear power plant.
Due to the earthquake, the external power to the reactors had been cut off which lead the cooling systems to fail.
As a result, the reactor overheated which finally led to hydrogen explosions which damaged some reactor buildings.
Since significant amounts of radioactivity had been released in this process, around half a million people had to be evacuated.
Conclusion
Nuclear energy is one of the most preferred strategies to produce electricity since it is relatively cheap.
Industries thus like to advocate for this energy source.
However, nuclear energy and the resulting nuclear waste also has significant downsides.
The production of nuclear waste in large amounts as well as potential nuclear accidents are a crucial threat to our environment.
Small mistakes in the handling of radioactive substances can cause catastrophic outcomes.
Therefore, we should consider the transition from nuclear to renewable energy sources.
This transition process is already discussed by many governments, however, it will take quite a long time to abandon nuclear energy completely.
In order to avoid nuclear waste and the adverse consequences, we should financially support our best researchers and work together to make this transition process feasible already in the near future.
You want to learn even more about nuclear energy? Check out the pros and cons of nuclear power.
Sources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radioactive_waste
https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/nuclear-waste

About the author
My name is Andreas and my mission is to educate people of all ages about our environmental problems and how everyone can make a contribution to mitigate these issues.
As I went to university and got my Master’s degree in Economics, I did plenty of research in the field of Development Economics.
After finishing university, I traveled around the world. From this time on, I wanted to make a contribution to ensure a livable future for the next generations in every part of our beautiful planet.
Wanna make a contribution to save our environment? Share it!