“I believe our biggest issue is the same biggest issue that the whole world is facing, and that’s habitat destruction.”
Steve Irwin, Scientist
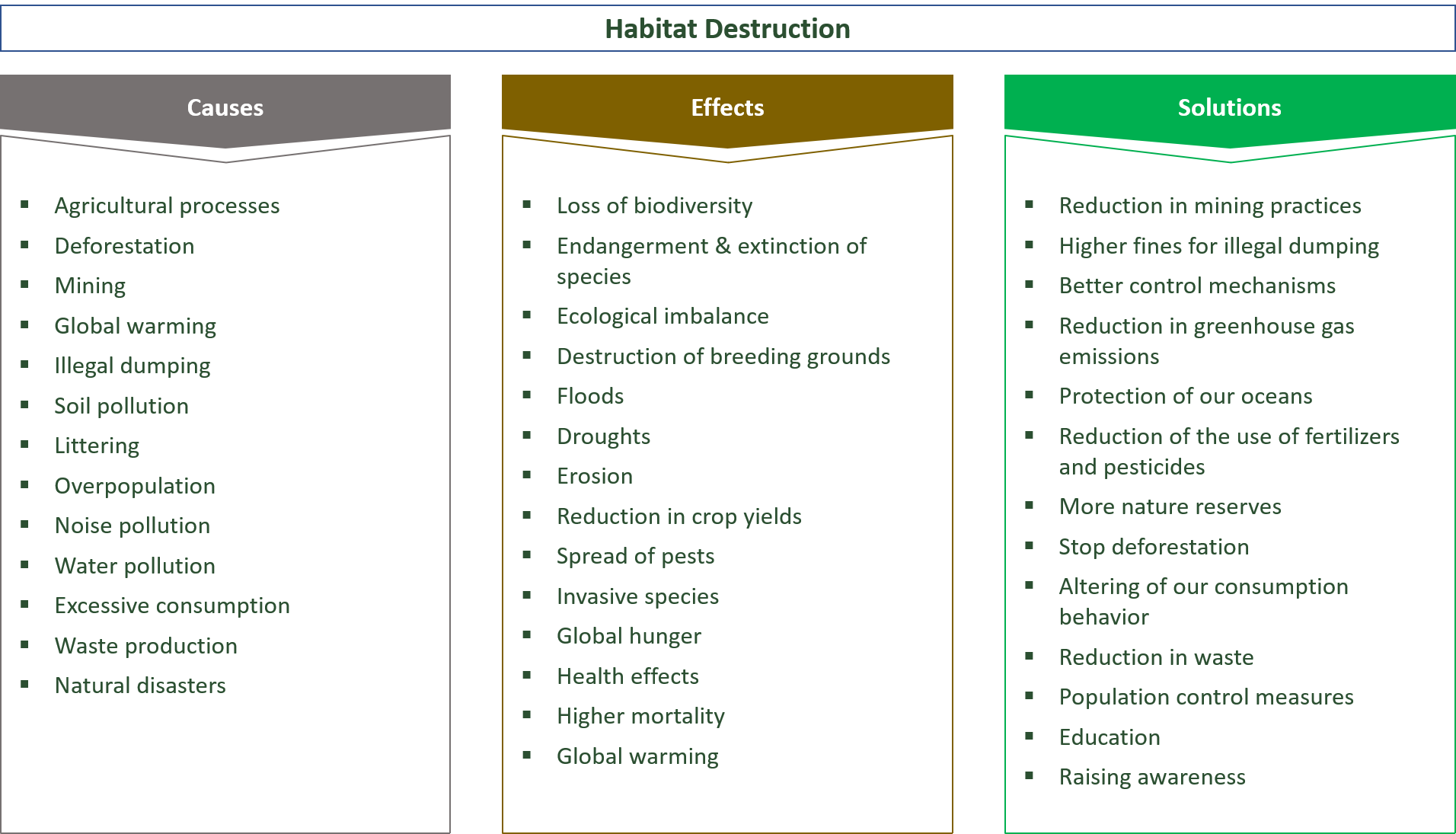
Habitat Destruction: Causes, Effects & Solutions
The destruction of habitats (also sometimes referred to as habitat loss or habitat reduction) can be defined as a state in which the natural living conditions of natural habitats are no longer suitable to support native species.
This implies that over time, many animal and plant species may die off.
Most of the habitat destruction comes from human interventions.
In this article, the causes, effects and solutions for habitat destruction are examined.
Audio Lesson
Contents
Causes for Habitat Destruction
- Agricultural processes
- Deforestation
- Mining
- Global warming
- Illegal dumping
- Soil pollution
- Littering
- Overpopulation
- Noise pollution
- Water pollution
- Excessive consumption
- Waste production
- Natural disasters
Agricultural processes
Agriculture can be a main cause of habitat destruction.
In order to plant large amounts of crops or to produce plenty of meat, large areas of land have to be used.
Many farmers try to expand their farming land on a continuous basis.
However, by expanding farming, many animals have to relocate and find new habitats, which may lead to a decrease in the population of those animal species.
Many plants may die off since they simply cannot relocate that quickly.
Deforestation
Deforestation is a significant reason for the destruction of habitats.
This can be seen in the Amazon Rainforest where farmers intentionally burn down the forest around their farms in order to get more space for farming purposes.
Even though this might be beneficial in financial terms for the individual farmer, it implies serious habitat destruction and hurts a variety of animal and plant species.
Mining
Since our technology advances quite rapidly, we as humanity are quite dependent on metals that are necessary for the production of computers and smartphones.
However, in order to extract those precious resources, large areas of land have to be used for mining purposes.
In turn, this implies significant destruction of habitats of many animal and plant species.
Global warming
In our industrial processes, large amounts of greenhouse gases are emitted into the atmosphere.
In turn, those greenhouse gases contribute to the global warming issue.
If sea levels increase due to global warming, a significant fraction of our global animal and plant species will lose their natural living conditions.
Moreover, also the increasing air temperature will lead to huge losses of habitats, since some areas, especially in hot and dry climate zones, will run out of water and animals and plants will no longer be able to survive under those extreme circumstances.
Illegal dumping
The dumping of waste in forests, rivers, lakes or the ocean is a serious environmental problem.
Especially in poor developing countries with rather lax waste disposal regulations and low control mechanisms, companies often dispose their industrial waste into nearby water bodies or forests, since it is quite convenient to get rid of the waste in this manner.
However, this implies significant contamination of the environment and can imply the destruction of habitats of the local flora and fauna.
Soil pollution
Through agricultural processes or the illegal dumping of industrial waste, the soil may become polluted in a serious manner.
Since plants are usually quite sensitive to changes in their natural living conditions, chances are that many plant species will significantly decrease in population and natural habitats may be altered or even destroyed.
Littering
Littering may be another cause of habitat destruction.
In our nowadays society, many people seem not to care about our environment at all.
They often dispose their cigarettes or other waste items right where they stand into nature.
This can be observed if you go for a walk in the forests.
Plenty of waste is disposed into our forests on a regular basis.
In turn, this leads to changes in the natural living conditions of many animal and plant species since those waste items often cause pollution of many sorts and may destroy habitats of those pollution levels become too high.
Overpopulation
Another reason for the destruction of habitats is overpopulation.
Our world population increases at an alarming rate.
Until the end of the century, there could be over 10 billion people populating our planet.
In order to supply enough food and resources for all those people, large areas of land have to be used for farming and mining purposes.
However, this also implies that many natural habitats that are currently used by animals and plants will be altered and may become destroyed over time.
Noise pollution
Many of our industrial processes imply some noise pollution.
Especially for animals that are quite sensitive to noise distractions, the construction of those industrial plants may force those animals to leave the respective areas and to search for a new home.
Water pollution
Our water bodies are polluted every day with large amounts of plastic waste and other harmful materials.
However, at one point in time when pollution levels become too high, the marine ecosystems may get out of balance and natural habitats may no longer be suitable for animals and plants and may become kind of an underwater desert.
Excessive consumption
Our consumption levels also play a significant role in the process of habitat destruction.
Since our material goods have to be produced through the use of resources like metals or other elements, our high consumption levels also imply a high demand for resources.
However, those resources have to be mined out of the ground, which implies the destruction of large habitats.
Waste production
Our excessive consumption levels also imply the production of large amounts of waste, which we have to get rid of somehow.
In order to get rid of this waste, it either has to be burned or disposed into landfills.
The burning of waste implies the emission of large amounts of greenhouse gases into our atmosphere, which in turn contributes to global warming.
The disposal of waste into landfills may lead to serious soil and groundwater pollution.
All this may contribute to significant habitat destruction.
Natural disasters
Also through natural disasters, large areas of land may be destroyed.
For instance, through earthquakes or tsunamis, whole regions may be flooded.
In turn, this also implies the destruction of natural habitats, since many animals and plants may no longer be able to survive due to these adverse conditions.

Effects of the Destruction of Habitats
- Loss of biodiversity
- Endangerment & extinction of species
- Ecological imbalance
- Destruction of breeding grounds
- Floods
- Droughts
- Erosion
- Reduction in crop yields
- Spread of pests
- Invasive species
- Global hunger
- Health effects
- Higher mortality
- Global warming
Loss of biodiversity
The destruction of habitats can lead to a serious loss of biodiversity.
Many animal species may have to leave if their natural ecosystems get destroyed.
Since plants cannot relocate, they might simply die off if their natural living conditions have been altered too much.
Over time, there may be a serious decline in the population of many animal and plant species due to habitat destruction.
Endangerment & extinction of species
In extreme cases, the destruction of habitats may also lead to the endangerment or even to the extinction of species.
Especially for species that only live in a few different places on our planet, if those areas get destroyed, chances are that those species may become extinct sooner or later.
Ecological imbalance
Ecosystems are quite complex organisms with myriads of interdependencies.
If one species becomes extinct, there could be several adverse effects on other predator or prey species.
In turn, whole ecosystems may get out of balance due to the extinction of only a few species.
In the worst case, this ecological imbalance may lead to desertification and therefore to a huge decline in biodiversity.
Destruction of breeding grounds
In order to be able to sustain their population, many animal and plant species rely on their natural ecosystems.
If the conditions in those ecosystems become altered or if habitats are destroyed due to human intervention, chances are that also the breeding grounds for may species get destroyed, which may lead to a significant decline in population of many animal and plant species.
Floods
Through deforestation and other human interventions, floods may become more probable.
In turn, many natural environments may be destroyed through floods.
In turn, many animals and plants may either drown or suffer from ecological imbalance in the long run.
Droughts
The destruction of habitats may also cause serious droughts.
For instance, forests are natural water storage spaces.
Through deforestation, those water storages may vanish and the chances for droughts may increase.
Erosion
Through the destruction of natural habitats, also the chances for erosions increase.
For instance, if forests are cut down, the roots of those trees are no longer able to hold the soil together and in times of heavy rainfalls, erosions become much more probable.
Reduction in crop yields
Through the destruction of habitats, also crop yields may become lower over time.
While in the short run, crop yields could be increased through deforestation and the use of excessive fertilizer and pesticides, in the long run, the ecological imbalance may lead to lower crop yields and to serious hunger among the local population, especially in poor regions of our planet.
Moreover, since many insects may decline in population, the pollination of plants may become much more difficult, which may further decrease crop yields significantly.
Spread of pests
Through the destruction of habitats and the farming of large areas of land with monocropping, the chances for the spread of pests increases dramatically.
Those pests may significantly decrease the crop yields of farmers, which in turn may lead to serious poverty for the local population.
Invasive species
The destruction of natural habitats may also lead to the spread of invasive species.
Our ecosystems have found a natural balance over millions of years.
However, due to the altering of natural living conditions from human interventions, these ecosystems may now become vulnerable and invasive species may enter the ecosystems, which may in turn lead to a decline of local species and ecosystems may get out of balance.
Global hunger
Due to the decrease in crop yields as a result of habitat destruction, millions of people all over the world may suffer from hunger and starvation.
Especially in poor regions where the local population is dependent on the crop yields of farmers as their main source of food, decreases in crop yields may lead to undernutrition, which may even lead to the death of many people in extreme cases.
Health effects
Habitat destruction may also indirectly lead to serious health effects for humans.
For instance, if people suffer from a decline in crop yields due to the destruction of habitats, they may suffer from severe hunger.
In turn, their immune system will become quite weak, which may lead to serious health issues since their body will no longer be able to defend against bacteria or viruses in a sufficient manner.
Higher mortality
Due to starvation and health issues, the mortality in regions where habitat destruction is quite prevalent may be significantly higher compared to other areas.
This is especially true in poor regions of our planet where people rely on farming as their primary food source.
Global warming
Global warming can be a cause for the destruction of habitats, but it can also be a consequence of it.
For instance, trees are natural carbon dioxide storage spaces.
If those trees are cut or burned down and natural habitats are destroyed, those trees are no longer able to store carbon dioxide, which leads to the emission of large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which in turn implies the acceleration of global warming.

Solutions for Habitat Destruction
- Reduction in mining practices
- Higher fines for illegal dumping
- Better control mechanisms
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
- Protection of our oceans
- Reduction of the use of fertilizers and pesticides
- More nature reserves
- Stop deforestation
- Altering of our consumption behavior
- Reduction in waste
- Population control measures
- Education
- Raising awareness
Reduction in mining practices
In order to prevent habitat destruction, we should significantly reduce our global mining practices.
By introducing stricter laws in the context of mining, we could preserve more habitats and ensure proper natural living conditions for many animals and plants.
Higher fines for illegal dumping
Illegal dumping is still a big problem, especially in poor developing countries with low fines.
Thus, especially in those countries, fines should be increased significantly so that the incentive for illegal dumping decreases and the destruction and pollution from illegal dumping practices could be lowered.
Better control mechanisms
In the context of illegal dumping and pollution, also better control mechanisms are necessary in order to protect our natural habitats.
If there are high fines but companies that engage in illegal dumping know that there are no controls, they will continue to do so.
Thus, better control mechanisms in combination with higher fines are necessary to efficiently fight illegal dumping and the resulting pollution in order to prevent natural habitat destruction.
Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
Since our greenhouse gas emissions contribute to global warming and global warming is a key factor for the destruction of habitats on a global scale, it is crucial that we significantly reduce our greenhouse gas emissions.
One important step to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is the transition from fossil to renewable energy sources, which is already on the agenda of many industrialized countries.
Protection of our oceans
Since our oceans are habitats for myriads of animals, corals and plant species, it is crucial to protect those water bodies.
In many countries all over the world, plenty of waste is still disposed into our oceans, which leads to serious ocean pollution and to the destruction of habitats of many animals and plants.
Thus, it is crucial that governments around the world pay close attention to this issue and take measures in order to reduce ocean dumping.
Reduction of the use of fertilizers and pesticides
Since the excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides implies serious soil pollution, which in turn contributes to the destruction of habitats, farmers should reduce their use of those substances in order to preserve natural habitats and also to protect our soil as well as our groundwater.
More nature reserves
In order to preserve our natural habitats in the future, governments around the world should create more nature reserves that should protect our animal and plant species from human interventions like mining or other practices that could potentially harm our environment.
Stop deforestation
Since our forests, especially our tropical rainforests, are natural habitats of the majority of all animal and plant species on our planet, it is crucial to stop deforestation and therefore to preserve those precious natural ecosystems.
Only then will we be able to sustain biodiversity and ensure the natural balance of our planet.
Altering of our consumption behavior
Every one of us can contribute to the preservation of natural habitats by changes in our consumption behavior.
In our current society, everyone wants to have the newest things, the hippest clothes, the latest electronics and so on.
However, this also implies that we use our resources in a quite inefficient manner.
By changing our consumption behavior and use our old things longer, we can reduce our resource consumption, which in turn would lower the need for mining and other practices that imply the destruction of natural habitats.
Reduction in waste
Since our waste often ends up in our ocean or has to be burned which leads to significant greenhouse gas emissions, it is crucial to reduce our overall waste production in order to protect our natural habitats.
You can reduce your waste production by reducing your overall consumption.
Moreover, you should try to reuse old things.
For instance, you could give away your old things to family and friends who might still want to use them or you could also donate them to charity.
If no one wants to have your old stuff, at least make sure to separate your waste properly in order to make it suitable for efficient recycling.
Population control measures
Since our growing world population implies an increasing overall consumption, waste production and greenhouse gas emissions which in turn contribute to the destruction of natural habitats, countries all over the world should consider measures in order to reduce the number of births so that the total number of people could be lowered in the long run.
For instance, this could be done through a one-child policy or other population control measures.
However, population control is a quite controversial topic and there are many pros and cons regarding population control.
Education
Education is crucial in order to solve several sorts of problems.
This is also true when it comes to the destruction of natural habitats.
Many people simply do not know at all how their actions impact our environment.
Therefore, it is crucial to educate the general public but also our children that their actions matter in the context of habitat destruction.
Thus, this education should start quite early in school so that children get aware of the problem and take measures in order to preserve our natural habitats.
These children may also convince their parents to act more eco-friendly, which may even improve the positive impact of the education measures even further.
Raising awareness
It is also crucial that you raise the awareness on the topic of habitat destruction if possible.
For instance, if you see people around you who act in an irresponsible ecological manner, you could point out to them how important it is to reduce our pollution levels in order to preserve our natural habitats.
By doing so, you might convince some people and therefore multiply your positive environmental impact.
Conclusion
Habitat destruction is a serious environmental problem.
Due to our excessive consumption of material goods, large areas of land are used for mining and other purposes which implies significant destruction of habitats of a variety of animal and plant species.
It is therefore crucial that every one of us makes his or her contribution in order to preserve our natural habitats.
Also, governments around the world have to set strict regulations in order to preserve those natural living areas.
Only then will it be possible to sustain biodiversity and also to ensure the ecological balance on a global scale.
Sources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Habitat_destruction
https://wwf.panda.org/our_work/wildlife/problems/habitat_loss_degradation/
https://www.nwf.org/Educational-Resources/Wildlife-Guide/Threats-to-Wildlife/Habitat-Loss
https://blog.nationalgeographic.org/2019/09/25/the-global-impacts-of-habitat-destruction/

About the author
My name is Andreas and my mission is to educate people of all ages about our environmental problems and how everyone can make a contribution to mitigate these issues.
As I went to university and got my Master’s degree in Economics, I did plenty of research in the field of Development Economics.
After finishing university, I traveled around the world. From this time on, I wanted to make a contribution to ensure a livable future for the next generations in every part of our beautiful planet.
Wanna make a contribution to save our environment? Share it!